Networking and Protocols Basics
- Networking refers to how devices ie: Computers, Servers, and Smartphones communicate over a network ie: The internet or local area networks. This communication relies on protocols or agreed-upon rules that define how data is transmitted and received.
HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
-
HTTP is the primary protocol for transmitting web content from servers to browsers.
-
It follows a request-response model, where a client (like a browser) sends an HTTP request, and a server responds with the requested data (usually HTML, CSS, JavaScript, or JSON).
Features
HTTP Methods
-
GET - Retrieve data from a server. ie: Loading data from the server to a webpage.
-
POST - Send data to the server. ie: Submitting a form with new information.
-
PUT - Update an existing resource on the server. ie: Submitting a form with updated information.
-
DELETE - Remove a resource on the server. ie: Submitting a form to delete.
Here is complete list of HTTP Methods.
Stateless - Each request is independent and doesn’t retain information about previous requests unless cookies or sessions are used. In stateless systems, every request is independent, so the server doesn’t waste time or memory tracking sessions. This results in faster response times and lower memory usage.
Port - An HTTP port is a communication endpoint used by the HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP) to send and receive data between clients ie: Web browsers and servers ie: Web servers. Ports help computers differentiate between different types of network traffic. A server might run multiple services ie: Web, FTP, and Email on the same machine and each uses a different port. HTTP typically uses port 80.
Use Case - Browsing websites and making API requests without encryption.
HTTPS (HTTP Secure)
-
HTTPS is the secure version of HTTP. It uses encryption to protect data being transmitted between the client and server.
-
HTTPS encrypts data using SSL / TLS (Secure Socket Layer / Transport Layer Security), ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authentication.
-
HTTPS ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read or tampered with.
Features
HTTP Methods - Same as HTTP.
Stateless - Same as HTTP.
Port - Same as HTTP. HTTPS typically uses port 443.
Use Case - Online transactions, user logins, or any sensitive communication.
HTTP vs HTTPS

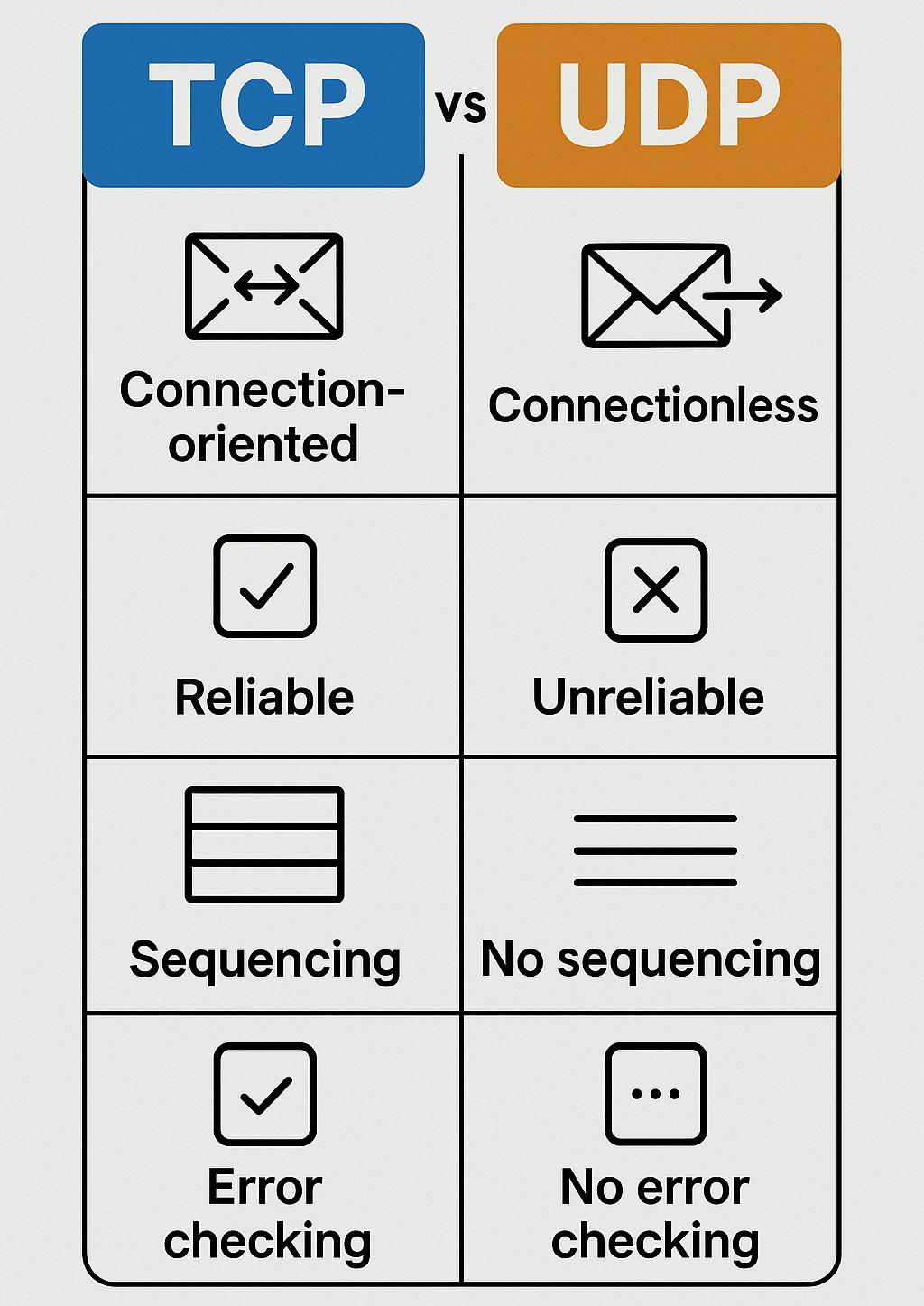
TCP / IP (Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol)
- TCP / IP is a set of communication protocols that governs how data is transmitted over the internet.
IP (Internet Protocol)
-
IP handles addressing and routing. Every device on the internet has an IP address ie: 192.168.1.1 that identifies it.
-
IP packets contain the source and destination IP addresses.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
-
TCP provides reliable communication by ensuring that data is delivered in the correct order without loss or duplication.
-
It is Connection-oriented, connection must be established before data transfer.
-
Data is split into segments, numbered, and reassembled at the destination.
-
Each data segment sent must be acknowledged to confirm it was received.
-
TCP ensures that corrupted data is detected and re-sent.
-
TCP identifies services by port numbers ie: Port 80 for HTTP.
-
Used by apps where data reliability is crucial, like web browsing, file transfers, or emails.
How TCP Works
-
Three-way handshake - TCP establishes a connection using a handshake process:
-
SYN - Client sends a synchronization request.
-
SYN-ACK - Server acknowledges.
-
ACK - Client confirms.
-
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
-
UDP is a connectionless protocol that sends data without establishing a connection.
-
UDP sends packets called datagrams directly to the destination without verifying whether they were received. There is no acknowledgment or retransmission of lost data.
-
It is Faster but less reliable than TCP because it does not perform any error-checking or acknowledgment.
-
UDP Uses the same port system as TCP ie: Port 53 for DNS.
-
It is suitable for real-time applications where speed is more important than reliability, such as:
-
Video streaming
-
Online gaming
-
Voice over IP (VoIP)
-
TCP vs UDP
Module Review
Click to start the definition to term matching quiz
Click to start the multiple choice quiz
Score: : 0 / 19 [0.00 %]
Question 1 of 19: What is the default port number for HTTP?